Transaction Management
What is Seata
Seata is an open source distributed transaction solution dedicated to providing high-performance and easy-to-use distributed transaction services. Seata will provide users with AT, TCC, SAGA and XA transaction modes to create a one-stop distributed solution for users.
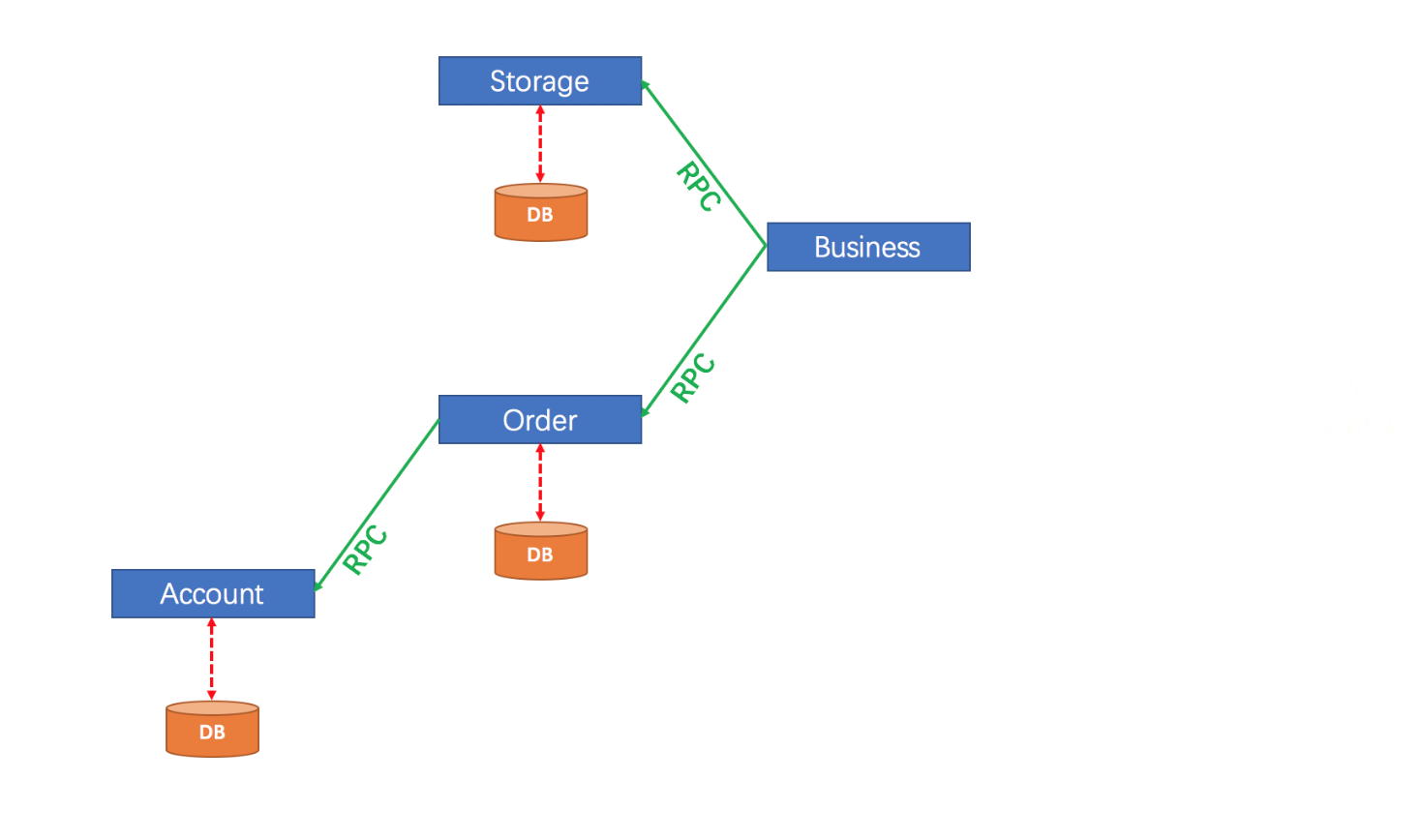
1. Example architecture description
The user purchases commodity business, and the whole business includes 3 microservices:
- Inventory service: deduction of the inventory quantity of a given item.
- Order service: Generate orders based on purchase requests.
- Account Services: deduction of the user account amount.
StorageService
public interface StorageService {
/**
* Deducted storage quantity
*/
void deduct(String commodityCode, int count);
}
OrderService
public interface OrderService {
/**
* Create Order
*/
Order create(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount);
}
AccountService
public interface AccountService {
/**
* Borrow from user account
*/
void debit(String userId, int money);
}
Two, the main business logic
BusinessService
public class BusinessServiceImpl implements BusinessService {
private StorageService storageService;
private OrderService orderService;
/**
* Purchasing
*/
public void purchase(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
// Deduct storage amount
storageService.deduct(commodityCode, orderCount);
// Create Order
orderService.create(userId, commodityCode, orderCount);
}
}
StorageService
public class StorageServiceImpl implements StorageService {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public void deduct(String commodityCode, int count) {
// Modify the database: deduct the amount of storage
jdbcTemplate.update("update storage_tbl set count = count - ? where commodity_code = ?",
new Object[]{count, commodityCode});
}
}
OrderService
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
private AccountService accountService;
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public Order create(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
// calculate the amount
int orderMoney = calculate(commodityCode, orderCount);
// The amount deducted from the user account
accountService.debit(userId, orderMoney);
// Modify the database: create a new order
final Order order = new Order();
order.userId = userId;
order.commodityCode = commodityCode;
order.count = orderCount;
order.money = orderMoney;
KeyHolder keyHolder = new GeneratedKeyHolder();
jdbcTemplate. update(con -> {
PreparedStatement pst = con. prepareStatement(
"insert into order_tbl (user_id, commodity_code, count, money) values (?, ?, ?, ?)",
PreparedStatement. RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
pst.setObject(1, order.userId);
pst.setObject(2, order.commodityCode);
pst.setObject(3, order.count);
pst.setObject(4, order.money);
return pst;
}, keyHolder);
order.id = keyHolder.getKey().longValue();
return order;
}
}
AccountService
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public void debit(String userId, int money) {
// Modify the database: deduct the amount from the user account
jdbcTemplate.update("update account_tbl set money = money - ? where user_id = ?", new Object[]{money, userId});
}
}
3. Quick start example
Step 1: Download the source code
git clone -b master https://github.com/apache/dubbo-samples.git
cd ./dubbo-samples-transaction/
Step 2: Start Seata-Server and MySQL through docker-compose
In this example, we use docker-compose to quickly pull up services like seata-server and mysql.
cd src/main/resources/docker
docker-compose up
Step 3: Build use cases
Execute the maven command to package the demo project
mvn clean package
Step 4: Start AccountService
java -classpath ./target/dubbo-samples-transaction-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar org.apache.dubbo.samples.starter.DubboAccountServiceStarter
Step 5: Start OrderService
java -classpath ./target/dubbo-samples-transaction-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar org.apache.dubbo.samples.starter.DubboOrderServiceStarter
Step 6: Start StorageService
java -classpath ./target/dubbo-samples-transaction-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar org.apache.dubbo.samples.starter.DubboStorageServiceStarter
Step 7: Start BusinessService
java -classpath ./target/dubbo-samples-transaction-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar org.apache.dubbo.samples.starter.DubboBusinessTester
4. Example core process
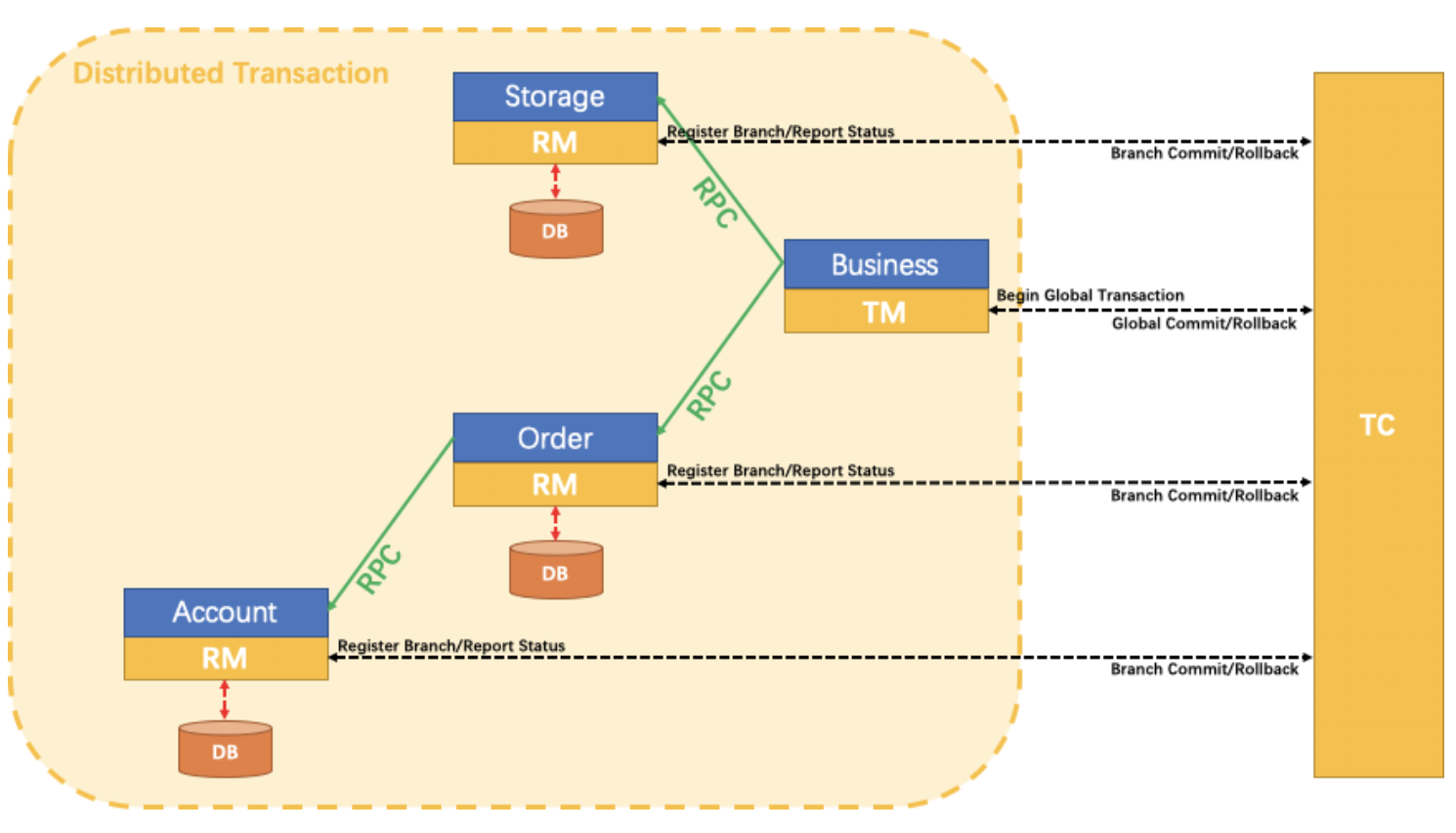
Step 1: Modify the business code
Here only one line of annotation @GlobalTransactional is required to be written on the method of the business initiator:
@GlobalTransactional
public void purchase(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
…
}
Step 2: Install the database
- Requirements: MySQL (InnoDB storage engine).
Tips: In fact, the 3 microservices in the example require 3 independent databases, but for convenience we use the same physical database and configure 3 logical connection strings.
Change the database url, username and password in the following xml files
dubbo-account-service.xml dubbo-order-service.xml dubbo-storage-service.xml
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://x.x.x.x:3306/xxx" />
<property name="username" value="xxx" />
<property name="password" value="xxx" />
Step 3: Create undo_log table for Seata
UNDO_LOG This table is used in Seata’s AT mode.
-- Note that when the Seata version is upgraded to 0.3.0+, the normal index will be changed to a unique index.
CREATE TABLE `undo_log` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`branch_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`xid` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`context` varchar(128) NOT NULL,
`rollback_info` longblob NOT NULL,
`log_status` int(11) NOT NULL,
`log_created` datetime NOT NULL,
`log_modified` datetime NOT NULL,
`ext` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `ux_undo_log` (`xid`,`branch_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
Step 4: Create related business tables
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `storage_tbl`;
CREATE TABLE `storage_tbl` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`commodity_code` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`count` int(11) DEFAULT 0,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY (`commodity_code`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `order_tbl`;
CREATE TABLE `order_tbl` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`commodity_code` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`count` int(11) DEFAULT 0,
`money` int(11) DEFAULT 0,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `account_tbl`;
CREATE TABLE `account_tbl` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`money` int(11) DEFAULT 0,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
Step 5: Start the Seata-Server service
- Download the server package, unzip it.
Usage: sh seata-server.sh(for linux and mac) or cmd seata-server.bat(for windows) [options]
Options:
--host, -h
The host to bind.
Default: 0.0.0.0
--port, -p
The port to listen.
Default: 8091
--storeMode, -m
log store mode: file, db
Default: file
--help
e.g.
sh seata-server.sh -p 8091 -h 127.0.0.1 -m file
